Wheel bearings have a very important job – enabling the rotation of your wheels. They make sure your wheels run smoothly with minimal friction. They also maintain correct wheel tracking and can even play a role in providing your vehicle’s drive systems with wheel speed sensor signals.
gina fitness desnuda películas para adolescentes oximetolona ciclo deltoides mediales – fitness at home – ejercicios en vídeo gratuitos
Over the years, three generations of wheel bearings have been developed. In our on-demand webinar, our experts take you inside all three generations to provide expert service advice and must-know installation procedures.
One side of the bearing rotates with the wheel while the other side is fixed to the suspension. The rolling elements in bearings carry vehicle load and ensure minimal-friction rotation between the inner and outer races. In automotive bearings, there are two types of rolling elements: ball bearings and roller bearings.
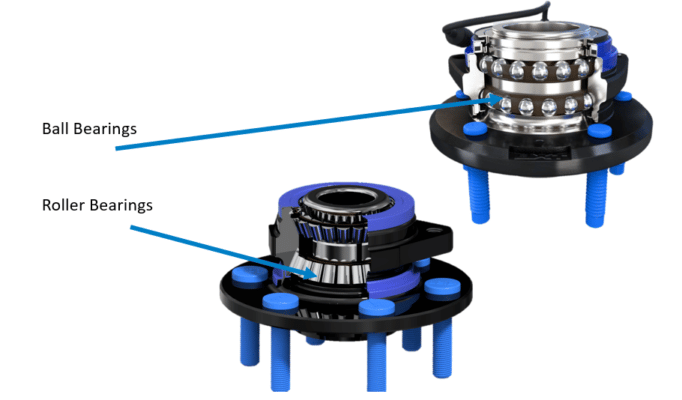
Ball bearings are used in applications where speed is more important than load. They have a small point of contact, which provides less rolling resistance and lighter load carrying capabilities.
Roller bearings, on the other hand, have a large point of contact, which makes them ideal for carrying higher loads. These bearings have many shapes and come in cylindrical, spherical, tapered and needle styles.
Wheel bearings have evolved and additional functions have been integrated into the assembly.
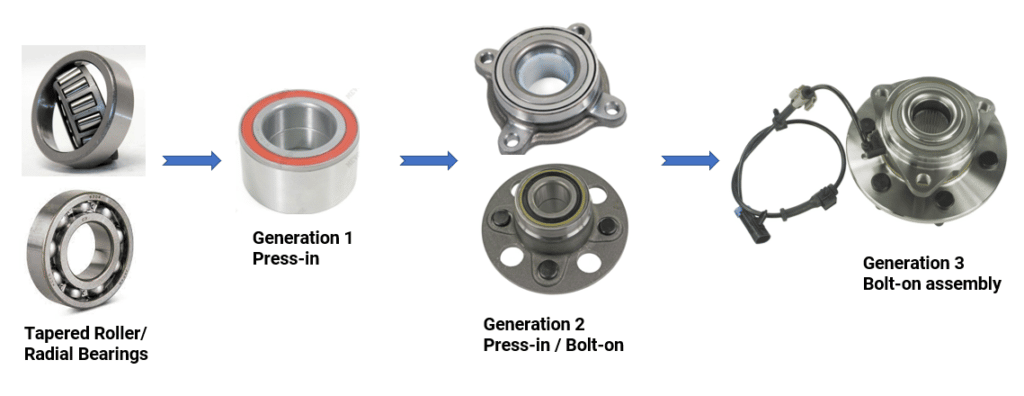
GENERATION 1: For driven or non-driven wheels
Are still installed on some import vehicles
Use a compact double-row design which cannot be disassembled
Need a spindle or axle thru-pin to set preload and keep assembly together
Are pre-lubricated and maintenance free
May feature an ABS encoder ring as one of the seals
Installation Tips
Use caution when pressing corresponding components into place
Ensure ABS encoder is undamaged and oriented correctly prior to pressing into the knuckle
Make sure the bearing has seated itself fully and that any required snap rings are also fully seated
Always tighten the axle or spindle nuts to the proper specification, since that will set the preload on the bearing
GENERATION 2: Typically used on non-driven wheels (but there are some driven applications)
Use compact double-row ball bearings which cannot be disassembled
Feature an additional hub or mounting flange with a rotating inner or outer ring
Are pre-lubricated and maintenance free
May feature an ABS encoder ring
Installation Tips
Install is similar to Gen 1 bearings but with one mounting flange pre-fitted
May require special tools to remove and install
GENERATION 3: For driven or non-driven wheels
Are most commonly used on today’s vehicles
Come as a complete unit with two flanges for securing to the knuckle and brake rotor/wheel
Feature compact double-row ball bearings or tapered rollers which cannot be disassembled
Premium variations will include roll-forming to set initial bearing preload
Are pre-lubricated and maintenance free
May feature an ABS encoder ring
Installation Tips
Properly clean the knuckle surface and bore to ensure the hub assembly gets well seated
If an axle passes through the hub, it is important the axle nut gets torqued to the proper specification
Do not omit the brake dust shield that fits between the hub and knuckle (It was factored into the entire geometry of the bearing and leaving it off could cause other issues.)
Some 4X4 front hub assemblies may use a vacuum hub locking system and particular attention needs to be paid to the seals
Overall, it is important to understand the type of bearing you are working with and to follow the proper installation procedures using the appropriate tools. Always tighten with a torque wrench to the correct torque specifications so the bearings are set to the proper preload.
For increased part service life and performance, the best wheel hub assemblies are engineered with a stiff roll-formed assembly, feature precision rolling elements and raceways, come pre-loaded with nanoceramic grease and are protected by advanced sealing and coating technology. They are also designed for a quick and complete fitting, with hardware and torque specs in the box.
2024-10-17